Dynamic Scheduling
Goal: To get high performance even with:
- long execution latencies (
fpinstructions that cause this) - long memory latencies (cache misses)
- long execution latencies (
A hardware approach to get ILP
In-Order v. Out-Of-Order#
- In-Order
- CPU is executing instructions in program order (ex: five-stage pipeline)
- Out-Of-Order
- Execute instructions as operands are ready
Tomasulo's Algorithm#
A technique that allows instructions to begin executing once their operands are ready
- Uses tags to identify data values instead of register numbers
- Maintain correct dependencies (for program correctness)
Need a decentralized register file
- Functional units (execution units or ALUs)
- Functional units get operands from buffers called reservation stations
- When a reservation station has all operands, then execution can start
Functional units output is placed on the common data bus
Three stages of Tomasulo Algorithm#
- Issue Stage
- Send an instruction to a reservation station if available, read any available operands from register file
- If all reservation stations are occupied, then stall the issue
- Execute Stage
- When all operands are available, begin execution
- Write Stage
- Write result to the common data bus
Key Aspects of Tomasulo Algorithm#
- Fetch still occurs in program order
- Execution occurs out-of-order
- Completion occurs out-of-order
- Ordering between Load/Stores is maintained (dependences can happen through memory)
- Before loads execute, the address is checked against stores currently in the processor
- Before stores execute, the address is checked against loads and stores currently in the processor
Common Data Bus#
- Send out the functional unit ID and the data value (tells reservation stations where the data came from)
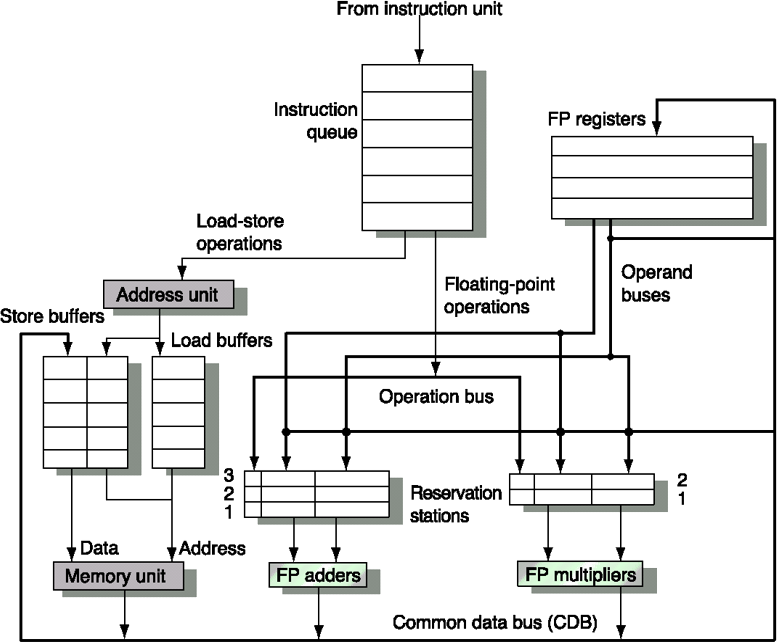
Reservation Station Components#
- - operation to perform in the unit (fp add → add/subtract) (fp mult → mult/div)
- - value of the source operands
- - reservation station producing the operand
- - holds memory address for loads/stores (address)
- Busy - indicates reservation station is occupied
- Register Result Status - tells which functional unit will write each register (clipboard)